
Testosterone is an important hormone made by the body that has an important role in sexual dimorphism, which is the differentiation of features into masculine or feminine. Testosterone is responsible for masculine features. The following sections will detail how testosterone works and how it affects facial features.
Testosterone leads to increased facial hair, wider and bigger jaw, wider and bigger nose, and higher facial width to height ratio.
The hormone testosterone is not only present in the male body, but females also have a certain amount of it as well. Yet; this amount is not nearly as abundant as in men. This abundance leads to a lot of changes: a wider jaw, for example, is one. Testosterone highly influences a person’s facial features, especially in puberty. It is also during this time that testosterone levels are very high.
What Is Testosterone?
The central production hub of testosterone is in the testicles. During puberty, hormones are at their peak levels. Testosterone is no exception. This hormone’s prevalence results in the growth of facial hair. It also results in denser muscles, broader shoulders, and a growth spurt. There are many other characteristics that we link to testosterone levels.
It is not surprising that testosterone also causes facial changes. Most of the changes we see come in the form of a wider jaw, sharper features, a more angular appearance. In general, men tend to have sharper features than women. Women generally have softer features that are more rounded out.
Apart from all that, testosterone is also vital in a man’s sex drive, which is why many people who lack testosterone seek treatment for it. A testosterone deficiency could seriously affect quality of life. Men who have high testosterone levels have a more robust sex drive compared to others.
Another application of testosterone is its use as an anabolic steroid. But, this type of use is generally frowned upon as it has negative health consequences and impacts your hairline. It enhances testosterone to above natural levels. It also usually comes with other components that could also negatively affect health.
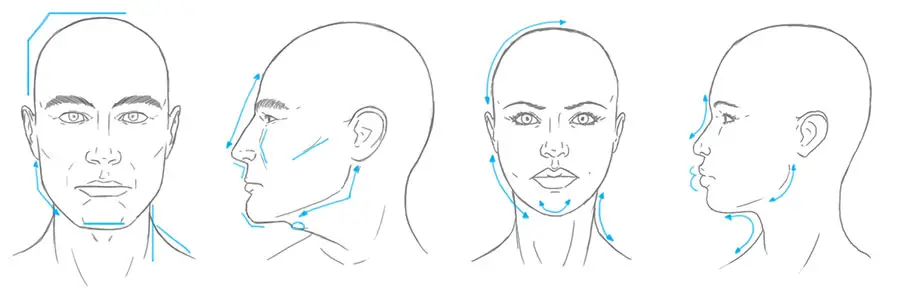
How Does Testosterone Affect Facial Features?
As a person grows from child to adult, their face changes and shifts. Children around 4-7 years old have a few parts that differentiate them as male or female. This observation excludes the primary sex organ. It is puberty that accentuates sexually dimorphic characteristics.
Facial Hair
Facial hair is one of the most significant changes to the face that occurs during puberty. Facial hair is not typically considered a “facial feature” such as the nose or eyes, but it is sexually dimorphic and contributes to a masculine facial appearance.
You will often see many male celebrities rocking their variations of a beard. In general, facial hair is a crucial masculine characteristic in most cases. Some men have trouble growing their facial hair, even if they have high testosterone levels. There are many other genetic components apart from testosterone that influences facial hair. If you can’t grow a full beard check out our minoxidil beard guide. We also recommend the Nick Bateman beard if you can grow a full beard.
The Jaw
Another one of the more masculine traits is a wide jaw. It is easy to notice that men, in general, have wider or broader jaws. Their jawlines are usually more defined than women. During puberty, the sharpness of a young man’s features starts to set in.
A child’s jaw is usually rounder and has some chubbiness to it. Over time, that goes away. The jaw and face then become sharper and have more angles. Although testosterone plays a role in this, it does not mean that only men have angular jaws. Angelina Jolie, for example, has a very wide jaw and distinctive jawline.
The Nose
Much like the jaw, men also have a wider nose compared to women. Barring ethnic differences, women usually have smaller and daintier noses compared to men. In this study by Marečková et al. (2011), the nose was a testosterone-mediated sex difference. It turns out that these features were most noticeably masculine, and they also had links to higher testosterone levels.
Other characteristics involve the chin and the forehead, which are usually different for men and women. But note that testosterone is not the only hormone that influences these characteristics. Instead, it is a mixture of hormones and genetics. But we cannot deny that testosterone affects facial features.
Take, for example, this study by Lefevre et al. (2013), where they studied facial metrics. The researchers concluded that face width to lower face height ratio positively relates to testosterone. Many other case studies come to the same conclusion. Read more about the facial width to height ratio here.
Testosterone Therapy (Hormone Replacement Therapy)
Many men resort to testosterone therapy to increase their testosterone levels. Most of them do this for the negative symptoms associated with low testosterone, such as the following:
1. Low Sex Drive
A low sex drive could affect men on more than just a superficial level. It could interfere with intimate relationships and come in the way of a good quality of life. It isn’t strange that many men would want to find a solution to this problem.
2. Fatigue
Another symptom or effect of low testosterone is fatigue. People with low testosterone have reported feeling tired despite getting an appropriate amount of rest and sleep. Intense chronic fatigue also comes with lower energy levels. As you may expect, being constantly fatigued is not ideal for optimal life functioning. Restoring testosterone levels to a healthy amount is necessary to achieve better energy.
3. Muscle Mass Deficiency
Low testosterone levels could also result in lower muscle mass. Testosterone is a hormone that also regulates muscle mass. Thus, some people use testosterone as an anabolic steroid to increase their muscle mass or at least have the ability to work out and see results like a normal person.
4. Mood Swings
As testosterone is a hormone that regulates many bodily processes, a person’s mental capacity is no exception. Low testosterone levels have links to depression and anger (Tsujimura, 2013). Increasing testosterone levels to a healthy amount could help a man cope with the different mood swings due to the hormone.
5. Bone Problems
A deficiency in bone density due to low testosterone levels could cause osteoporosis in men. This symptom occurs because of the scarce minerals and density of the bones.
6. Hair Loss
Testosterone is a hormone that also determines hair growth and conversely, a testosterone deficiency will cause hair loss problems. While hair loss is normal as a man ages, low testosterone levels could cause hair loss to come at an earlier stage.
The natural course of testosterone levels is to heighten at puberty and decrease gradually over time. A natural decrease in the body is completely fine and normal. However, problems arise when the decrease is rapid. A rapid decrease in testosterone levels could be due to tumors, injury to the testicles, cancer, HIV/AIDS. For most of these problems, hormone therapy is the solution.
But, hormone therapy is not the same as testosterone as steroids to build muscle mass. Testosterone replacement therapy only increases testosterone levels to a natural count. But, steroid use goes above and beyond this.
Unfortunately, most people will actually see increased hair loss on testosterone replacement given that androgens are the root cause of hair loss.

